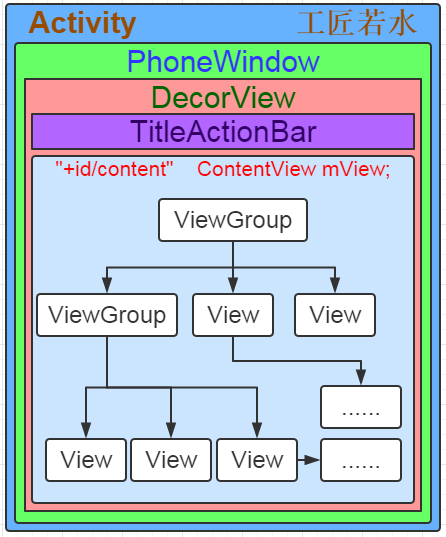
我们之前分析Window机制时已经清楚的理解了我们设置的View 就是DecorView的mContentParent下的View树
起点
WindowManagerGlobal
DecorView通过 WindowManager添加view到window显示与用户交互
而ViewRootImpl 是用来连接 WindowManager 和 DecorView 的桥梁
在 WindowManagerGlobal 的 addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow) 方法中,创建了 ViewRootImpl 对象,将 ViewRootImpl 和 DecorView 相关联 root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
Android中的任何一个布局、任何一个控件其实都是直接或间接继承自View实现的 这些View应该都具有相同的绘制流程与机制才能显示到屏幕上 每一个View的绘制过程都必须经历三个最主要的过程,也就是measure、layout和draw。
而整个view树的绘制就是通过ViewRootImpl将decorview绘制完成交由WindowManager在window上显示
ViewRootImpl
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
// 将 decorView 设置给全局的 mView
mView = view;
...
// 标记已经添加了 decorView
mAdded = true;
...
// 第一次发起布局,在添加到 WindowManager 之前
// 确保在接收其他系统事件之前完成重新布局
requestLayout();
...
// 利用 mWindowSession 以跨进程的方式向 WMS 发起一个调用,从而将DecorView 最终添加到 Window 上
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes, getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets, mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
}
...
}
}
}
这个源码方法的重点在与requestLayout(); 它是绘制步骤的关键我们继续深入
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
最终调用scheduleTraversals();
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
// 发送消息,调用 mTraversalRunnable
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
}
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
final TraversalRunnable mTraversalRunnable = new TraversalRunnable();
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// 内部调用了 performTraversals()
doTraversal();
}
}
在主线程调用doTraversal(); 最后在深入还是要看performTraversals()
private void performTraversals() {
// 计算 Activity 中 window 的宽高等等
...
if (!mStopped || mReportNextDraw) {
boolean focusChangedDueToTouchMode = ensureTouchModeLocally(
(relayoutResult&WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_IN_TOUCH_MODE) != 0);
if (focusChangedDueToTouchMode || mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth()
|| mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight() || contentInsetsChanged ||
updatedConfiguration) {
// 得到 view 宽高的规格
// mWidth 和 mHeight 即用来描述 Activity 窗口宽度和高度
// lp.width 和 lp.height 就是 DecorView 的宽高
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag, "Ooops, something changed! mWidth="
+ mWidth + " measuredWidth=" + host.getMeasuredWidth()
+ " mHeight=" + mHeight
+ " measuredHeight=" + host.getMeasuredHeight()
+ " coveredInsetsChanged=" + contentInsetsChanged);
// Ask host how big it wants to be
// 开始执行测量工作,测量是从这里发起的
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// Implementation of weights from WindowManager.LayoutParams
// We just grow the dimensions as needed and re-measure if
// needs be
int width = host.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = host.getMeasuredHeight();
boolean measureAgain = false;
// 检查是否需要重新测量
if (lp.horizontalWeight > 0.0f) {
width += (int) ((mWidth - width) * lp.horizontalWeight);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
measureAgain = true;
}
if (lp.verticalWeight > 0.0f) {
height += (int) ((mHeight - height) * lp.verticalWeight);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
measureAgain = true;
}
// 需要再次测量的话,就再执行一遍 performMeasure
if (measureAgain) {
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag,
"And hey let's measure once more: width=" + width
+ " height=" + height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
layoutRequested = true;
}
}
...
final boolean didLayout = layoutRequested && (!mStopped || mReportNextDraw);
boolean triggerGlobalLayoutListener = didLayout
|| mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes;
if (didLayout) {
// 执行布局工作,布局是从这里发起的
performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight);
...
if (!cancelDraw && !newSurface) {
if (mPendingTransitions != null && mPendingTransitions.size() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < mPendingTransitions.size(); ++i) {
mPendingTransitions.get(i).startChangingAnimations();
}
mPendingTransitions.clear();
}
// 执行绘制工作,绘制是从这里发起的
performDraw();
}
...
}
performTraversals() 方法的代码很长很长,但是我们关注点就可以放在三大流程上。其他的代码因为自己能力欠缺,并不能一一说出这些代码的作用。所以我们接下来就把重点放在:
1.getRootMeasureSpec
2.performMeasure
3.performLayout
4.performDraw
getRootMeasureSpec
windowSizeMayChange |= measureHierarchy(host, lp, res,
desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight);
在 measureHierarchy 方法中已经调用了 performMeasure 来进行测量 这里只是为了确定 window 的大小而做的测量辅助
在 measureHierarchy 中,确定了 DecorView 的 MeasureSpec 。其中 childWidthMeasureSpec 和 childHeightMeasureSpec 即为 DecorView 对应的 MeasureSpec 。
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
如果是 MATCH_PARENT ,那么对应的就是窗口大小;
如果是 WRAP_CONTENT ,那么不能超过窗口大小;
固定大小,那么就是大小就是传入的 lp.width/lp.height 了。
ViewGroup中 计算子 View 测量规格的 getChildMeasureSpec 方法
也是根据父容器的规格确定子容器
具体可用这张图表示

总结:对于 DecorView 来说,其 MeasureSpec 是由窗口的大小和自身的 LayoutParams 来共同决定的;而对于普通的 View 来说,其 MeasureSpec 是由父容器的 MeasureSpec 和自身的 LayoutParams 共同决定的。
performMeasure
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
// 进行测量
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
在 performMeasure 中调用了 measure 方法。说到底,DecorView 只是一个View所以我们又要进入 View 类中去看下。
View 的 measure 方法内部是调用了 onMeasure
这里小提一下,我们都知道 DecorView 其实是一个 FrameLayout ,所以 onMeasure 应该在 FrameLayout 中去看
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
// 判断当前 framelayout 布局的宽高是否至少一个是 match_parent 或者精确值 ,如果是则置 measureMatchParent 为 false .
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
// 遍历不为 GONE 的子 view
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 对每一个子 View 进行测量
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 寻找子 View 中宽高的最大者,因为如果 FrameLayout 是 wrap_content 属性
// 那么它的宽高取决于子 View 中的宽高最大者
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
// 如果 FrameLayout 为 wrap_content 且 子 view 的宽或高为 match_parent ,那么就添加到 mMatchParentChildren 中
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
//设置测量结果
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
// 子View中设置为match_parent的个数
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
// 若 FrameLayout 为 wrap_content 且 count > 1
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 如果子 View 的宽度是 match_parent 属性,那么对 childWidthMeasureSpec 修改:
// 把 widthMeasureSpec 的宽度修改为:framelayout总宽度 - padding - margin,模式设置为 EXACTLY
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
// 否则就按照正常的来就行了
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
// 高度同理
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
//对于这部分的子 View 需要重新进行 measure 过程
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
其实总的来说重要的就只有遍历 child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec) 这个方法,这是将父容器的 measure 过程传递到子 View 中。
而子 View 被父容器调用了 measure 后,也会调用属于自己的 onMeasure 方法
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
在onMeasure源码中设置宽高尺寸 使用了getDefaultSize,我们在看下getDefaultSize的源码
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
//通过MeasureSpec解析获取mode与size 即前两位和后三十位
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
//父控件对子控件不加任何束缚,子元素可以得到任意想要的大小
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST://父控件为子View指定确切大小
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://父控件为子元素指定最大参考尺寸
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
若是 UNSPECIFIED ,则直接返回的就是 getSuggestedMinimumWidth/getSuggestedMinimumHeight 的值;
若是 AT_MOST/EXACTLY ,直接用的就是 specSize 。
而根据我们之前总结出来的表可知,只要 view 不指定固定大小,那么无论是 AT_MOST 还是 EXACTLY ,都是按照 parentSize 来的。
performLayout
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
基本可知,performLayout 是通过调用 DecorView 的 layout 方法来向下传递布局的。所以我们应该继续追踪 FrameLayout 的 layout 方法,其实就是 ViewGroup 的 layout 方法。
@Override
public final void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (!mSuppressLayout && (mTransition == null || !mTransition.isChangingLayout())) {
if (mTransition != null) {
mTransition.layoutChange(this);
}
// 调用 view 的 layout 方法
super.layout(l, t, r, b);
} else {
// record the fact that we noop'd it; request layout when transition finishes
mLayoutCalledWhileSuppressed = true;
}
}
在 ViewGroup 的 layout 方法中又调用了父类的方法 super.layout(l, t, r, b) 。所以我们又要到 View 类中去看。
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {
onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
// 当前布局的四个顶点
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
// 计算四个顶点的值,判断布局位置是否改变
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);//setOpticalFrame 的内部也是调用 setFrame 方法的。
// 如果视图的大小和位置发生变化,会调用onLayout()
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
// 空方法
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
if (shouldDrawRoundScrollbar()) {
if(mRoundScrollbarRenderer == null) {
mRoundScrollbarRenderer = new RoundScrollbarRenderer(this);
}
} else {
mRoundScrollbarRenderer = null;
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
// 调用布局位置改变监听器
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener> listenersCopy =
(ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener>)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT;
}
1.设置当前布局中的四个顶点;2.调用 setFrame 来设置新的顶点位置;3.调用 onLayout 方法;4.回调布局位置改变监听器;
在setFrame(l, t, r, b)判断大小是否改变 改变了就重绘 并回调相关接口
之后回调onLayout方法 因为decorview为framelayout进入其onLayout方法
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
layoutChildren(left, top, right, bottom, false /* no force left gravity */);
}
void layoutChildren(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, boolean forceLeftGravity) {
final int count = getChildCount();
final int parentLeft = getPaddingLeftWithForeground();
final int parentRight = right - left - getPaddingRightWithForeground();
final int parentTop = getPaddingTopWithForeground();
final int parentBottom = bottom - top - getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// 遍历子 view
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 子 view 的宽高
final int width = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
int childLeft;
int childTop;
// 得到子 view 的 gravity
int gravity = lp.gravity;
if (gravity == -1) {
gravity = DEFAULT_CHILD_GRAVITY;
}
final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection();
final int absoluteGravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity, layoutDirection);
final int verticalGravity = gravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK;
// 根据不同的 gravity 来计算 childLeft
switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
childLeft = parentLeft + (parentRight - parentLeft - width) / 2 +
lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.RIGHT:
if (!forceLeftGravity) {
childLeft = parentRight - width - lp.rightMargin;
break;
}
case Gravity.LEFT:
default:
childLeft = parentLeft + lp.leftMargin;
}
// 根据不同的 gravity 来计算 childTop
switch (verticalGravity) {
case Gravity.TOP:
childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin;
break;
case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL:
childTop = parentTop + (parentBottom - parentTop - height) / 2 +
lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin;
break;
case Gravity.BOTTOM:
childTop = parentBottom - height - lp.bottomMargin;
break;
default:
childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin;
}
// 调用子 view 的 layout 方法
child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height);
}
}
}
在 layoutChildren 中,遍历所有可见的子 View ,然后得到它们的宽高。
再根据不同的 gravity 来计算 childLeft 和 childTop ,最后调用 child.layout 来向子 View 传递下去。
子view根据四个顶点摆放在对应位置
performDraw
private void performDraw() {
if (mAttachInfo.mDisplayState == Display.STATE_OFF && !mReportNextDraw) {
return;
}
final boolean fullRedrawNeeded = mFullRedrawNeeded;
mFullRedrawNeeded = false;
mIsDrawing = true;
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "draw");
try {
// 调用 draw 方法,fullRedrawNeeded 为是否重新绘制全部视图
draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
} finally {
mIsDrawing = false;
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
...
}
private void draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
...
// dirty 表示需要绘制的区域
final Rect dirty = mDirty;
if (mSurfaceHolder != null) {
// The app owns the surface, we won't draw.
dirty.setEmpty();
if (animating && mScroller != null) {
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
return;
}
// 如果需要全部绘制,那么 dirty 就是整个屏幕了
if (fullRedrawNeeded) {
mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState = true;
dirty.set(0, 0, (int) (mWidth * appScale + 0.5f), (int) (mHeight * appScale + 0.5f));
}
...
// 调用 drawSoftware ,把绘制区域 dirty 传入
if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset, scalingRequired, dirty)) {
return;
}
...
}
private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff,
boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty) {
// Draw with software renderer.
final Canvas canvas;
try {
final int left = dirty.left;
final int top = dirty.top;
final int right = dirty.right;
final int bottom = dirty.bottom;
//锁定画布,由 dirty 区域决定
canvas = mSurface.lockCanvas(dirty);
// The dirty rectangle can be modified by Surface.lockCanvas()
//noinspection ConstantConditions
if (left != dirty.left || top != dirty.top || right != dirty.right
|| bottom != dirty.bottom) {
attachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState = true;
}
// TODO: Do this in native
canvas.setDensity(mDensity);
} catch (Surface.OutOfResourcesException e) {
handleOutOfResourcesException(e);
return false;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
Log.e(mTag, "Could not lock surface", e);
// Don't assume this is due to out of memory, it could be
// something else, and if it is something else then we could
// kill stuff (or ourself) for no reason.
mLayoutRequested = true; // ask wm for a new surface next time.
return false;
}
try {
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION || DEBUG_DRAW) {
Log.v(mTag, "Surface " + surface + " drawing to bitmap w="
+ canvas.getWidth() + ", h=" + canvas.getHeight());
//canvas.drawARGB(255, 255, 0, 0);
}
// If this bitmap's format includes an alpha channel, we
// need to clear it before drawing so that the child will
// properly re-composite its drawing on a transparent
// background. This automatically respects the clip/dirty region
// or
// If we are applying an offset, we need to clear the area
// where the offset doesn't appear to avoid having garbage
// left in the blank areas.
if (!canvas.isOpaque() || yoff != 0 || xoff != 0) {
canvas.drawColor(0, PorterDuff.Mode.CLEAR);
}
dirty.setEmpty();
mIsAnimating = false;
mView.mPrivateFlags |= View.PFLAG_DRAWN;
if (DEBUG_DRAW) {
Context cxt = mView.getContext();
Log.i(mTag, "Drawing: package:" + cxt.getPackageName() +
", metrics=" + cxt.getResources().getDisplayMetrics() +
", compatibilityInfo=" + cxt.getResources().getCompatibilityInfo());
}
try {
canvas.translate(-xoff, -yoff);
if (mTranslator != null) {
mTranslator.translateCanvas(canvas);
}
canvas.setScreenDensity(scalingRequired ? mNoncompatDensity : 0);
attachInfo.mSetIgnoreDirtyState = false;
// 调用 View 的 draw 方法
mView.draw(canvas);
drawAccessibilityFocusedDrawableIfNeeded(canvas);
} finally {
if (!attachInfo.mSetIgnoreDirtyState) {
// Only clear the flag if it was not set during the mView.draw() call
attachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState = false;
}
}
} finally {
try {
surface.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
Log.e(mTag, "Could not unlock surface", e);
mLayoutRequested = true; // ask wm for a new surface next time.
//noinspection ReturnInsideFinallyBlock
return false;
}
if (LOCAL_LOGV) {
Log.v(mTag, "Surface " + surface + " unlockCanvasAndPost");
}
}
return true;
}
最后调用了mView.draw(canvas);
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
(mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// 第一步,画背景
int saveCount;
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
drawBackground(canvas);
}
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
// 可能的话,跳过第二步和第五步
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// 第三步,画自己的内容
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// 第四步,画自己子 view 的内容
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// 第六步,绘制View的装饰,比如 scrollbar 等 (foreground, scrollbars)
onDrawForeground(canvas);
// 做完了,直接返回 we're done...
return;
}
/*
* Here we do the full fledged routine...
* (this is an uncommon case where speed matters less,
* this is why we repeat some of the tests that have been
* done above)
*/
boolean drawTop = false;
boolean drawBottom = false;
boolean drawLeft = false;
boolean drawRight = false;
float topFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float bottomFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float leftFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float rightFadeStrength = 0.0f;
// 第二步,保存 canvas 图层
int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft;
final boolean offsetRequired = isPaddingOffsetRequired();
if (offsetRequired) {
paddingLeft += getLeftPaddingOffset();
}
int left = mScrollX + paddingLeft;
int right = left + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight - paddingLeft;
int top = mScrollY + getFadeTop(offsetRequired);
int bottom = top + getFadeHeight(offsetRequired);
if (offsetRequired) {
right += getRightPaddingOffset();
bottom += getBottomPaddingOffset();
}
final ScrollabilityCache scrollabilityCache = mScrollCache;
final float fadeHeight = scrollabilityCache.fadingEdgeLength;
int length = (int) fadeHeight;
// clip the fade length if top and bottom fades overlap
// overlapping fades produce odd-looking artifacts
if (verticalEdges && (top + length > bottom - length)) {
length = (bottom - top) / 2;
}
// also clip horizontal fades if necessary
if (horizontalEdges && (left + length > right - length)) {
length = (right - left) / 2;
}
if (verticalEdges) {
topFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getTopFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawTop = topFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
bottomFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getBottomFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawBottom = bottomFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
}
if (horizontalEdges) {
leftFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getLeftFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawLeft = leftFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
rightFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getRightFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawRight = rightFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
}
saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount();
int solidColor = getSolidColor();
if (solidColor == 0) {
final int flags = Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG;
if (drawTop) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags);
}
if (drawBottom) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, null, flags);
}
if (drawLeft) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, top, left + length, bottom, null, flags);
}
if (drawRight) {
canvas.saveLayer(right - length, top, right, bottom, null, flags);
}
} else {
scrollabilityCache.setFadeColor(solidColor);
}
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// 第五步,绘制边缘效果和恢复图层
final Paint p = scrollabilityCache.paint;
final Matrix matrix = scrollabilityCache.matrix;
final Shader fade = scrollabilityCache.shader;
if (drawTop) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength);
matrix.postTranslate(left, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
p.setShader(fade);
canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p);
}
if (drawBottom) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * bottomFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(180);
matrix.postTranslate(left, bottom);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
p.setShader(fade);
canvas.drawRect(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, p);
}
if (drawLeft) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * leftFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(-90);
matrix.postTranslate(left, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
p.setShader(fade);
canvas.drawRect(left, top, left + length, bottom, p);
}
if (drawRight) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * rightFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(90);
matrix.postTranslate(right, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
p.setShader(fade);
canvas.drawRect(right - length, top, right, bottom, p);
}
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
// Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
onDrawForeground(canvas);
}
draw 过程大概有下面几步:
1.绘制背景:background.draw(canvas) ;
2.保存当前的图层信息(一般来说跳过);
3.绘制自己:onDraw(canvas) ;
4.绘制children:dispatchDraw(canvas) ;
在 dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) 中,遍历子 View ,然后调用 child.drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) 方法来执行子 View 的绘制流程,从而实现了绘制过程的向下传递。
在 draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) 中, 若没有缓存的话,那么调用 draw(canvas) ; 否则直接调用 dispatchDraw(canvas) 分发给子 View 适用于 ViewGroup
5.绘制边缘效果,恢复图层(一般来说跳过);
6.绘制前景装饰:onDrawForeground(canvas) 。
小结
我们把整个过程梳理以下
WindowManagerGlobal.addView()中代码root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display)创建了ViewRootImp WindowManagerGlobal.addView()中又调用了ViewRootImp的setView(view, wparams, panelParentView) 与decorview关联
-并在其中调用了requestLayout();
—-其中调用了 scheduleTraversals();
——其中在主线执行doTraversal();
———其中执行performTraversals();
———–其中执行了measureHierarchy根据view的大小调整window大小
———————————接着调用了performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
—————其中执行了DecorView.measure
——————-其中执行了DecorView.onMeasure
———————–其中循环执行了measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
———————– 1.ViewGroup.measure->ViewGroup.onMeasure -> ViewGroup.measureChildWithMargins
———————– 2.View.measure -> View.onMeasure
———————————接着调用了performLayout(lp, desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight);
—————其中执行了DecorView.layout 而viewgroup没有layout 进入view的layout
——————-其中执行了DecorView.onLayout 即FrameLayout.onLayout
———————–其中循环执行了child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height);根据四个点摆放位置
———————————接着调用了performDraw();
———–接着调用了ViewRootImp的draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
———–接着调用了ViewRootImp的drawSoftware
—————其中执行了DecorView.draw 而viewgroup没有draw 进入view的draw
——————-其中执行了DecorView.onDraw 即FrameLayout.onDraw 但是viewgroup没有这个方法 需要分发给子view执行
——————-接着执行了ViewGroup的dispatchDraw 循环执行drawChild(canvas, transientChild, drawingTime);
——————-其实就是viewgroup下子view执行draw 再执行onDraw()
注:DecorView 其实就是 FrameLayout
End.